Article
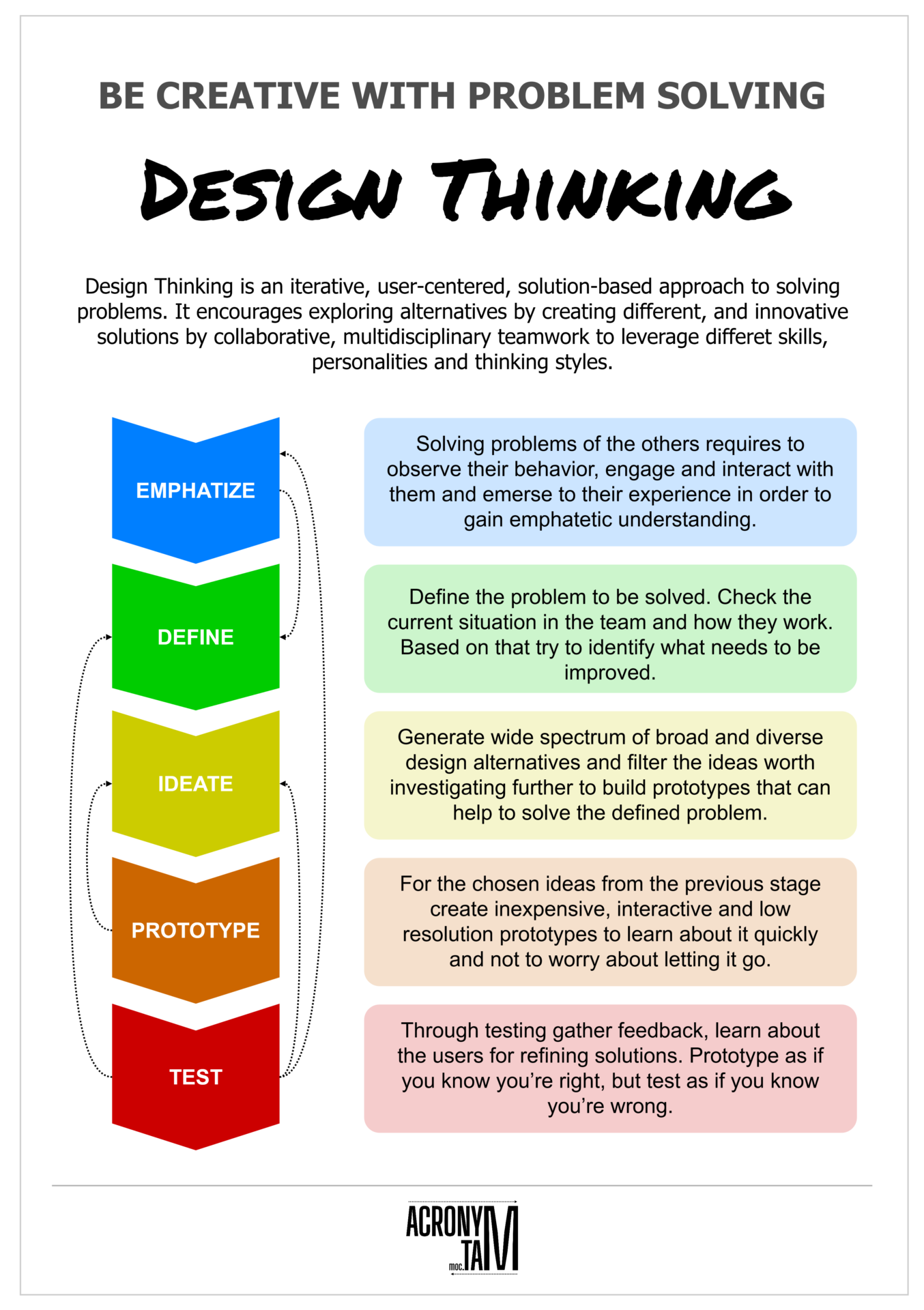
Design Thinking
Design Thinking is an iterative, user-centered, solution-based approach to solving problems. It encourages exploring alternatives by creating different, and innovative solutions by collaborative, multidisciplinary teamwork to leverage differet skills, personalities and thinking styles.
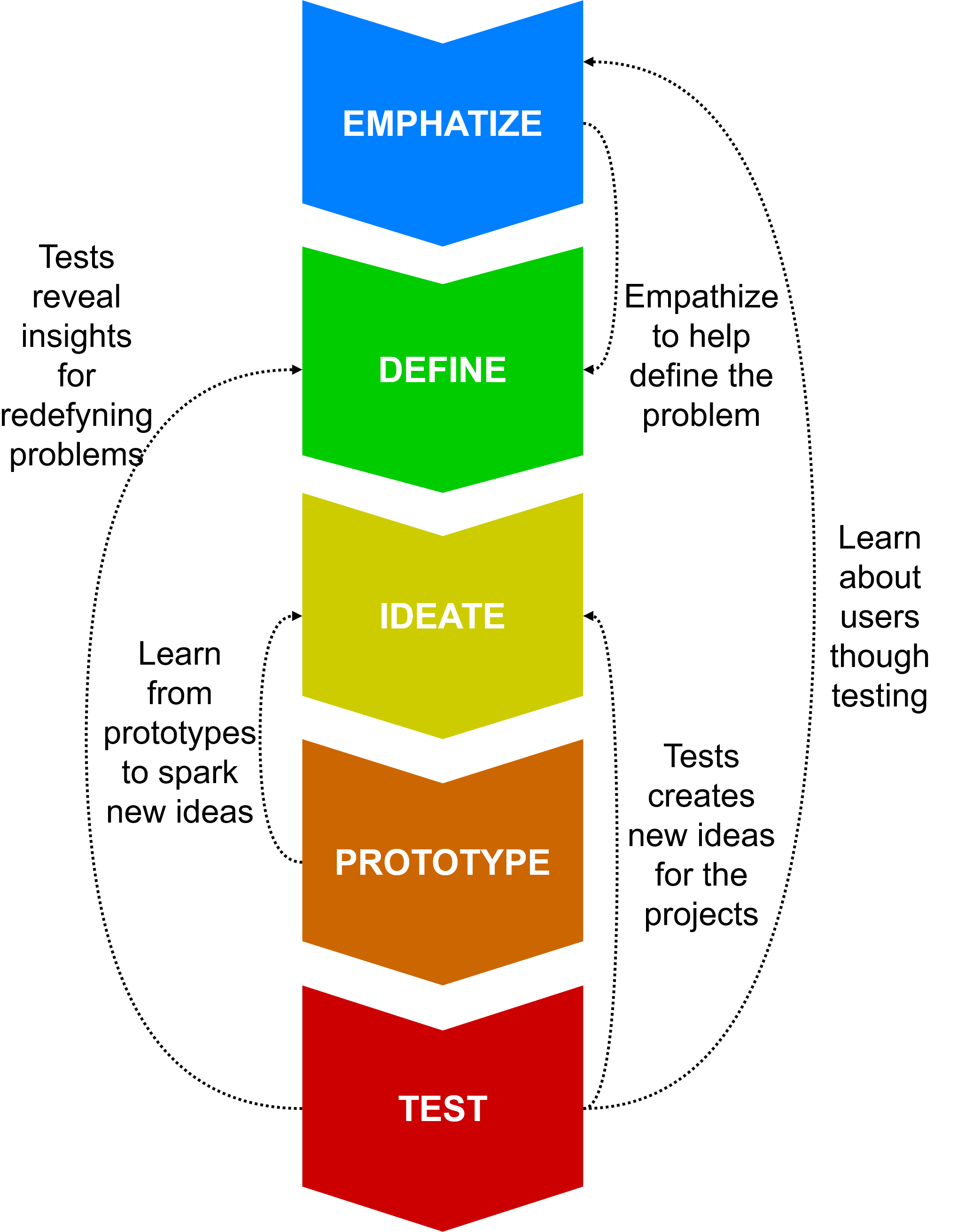
Emphatize
Solving problems of the others requires to observe their behavior, engage and interact with them and emerse to their experience in order to gain emphatetic understanding.
Define
Gather and sort the information from the previous stage and define the problem from users perspective which needs to be addressed, with no constraints from existing solutions.
Ideate
Generate wide spectrum of broad and diverse design alternatives and filter the ideas worth investigating further to build prototypes that can help to solve the defined problem.
Prototype
For the chosen ideas from the previous stage create inexpensive, interactive and low resolution prototypes to learn about it quickly and not to worry about letting it go.
Test
Through testing gather feedback, learn about the users for refining solutions. Prototype as if you know you’re right, but test as if you know you’re wrong.