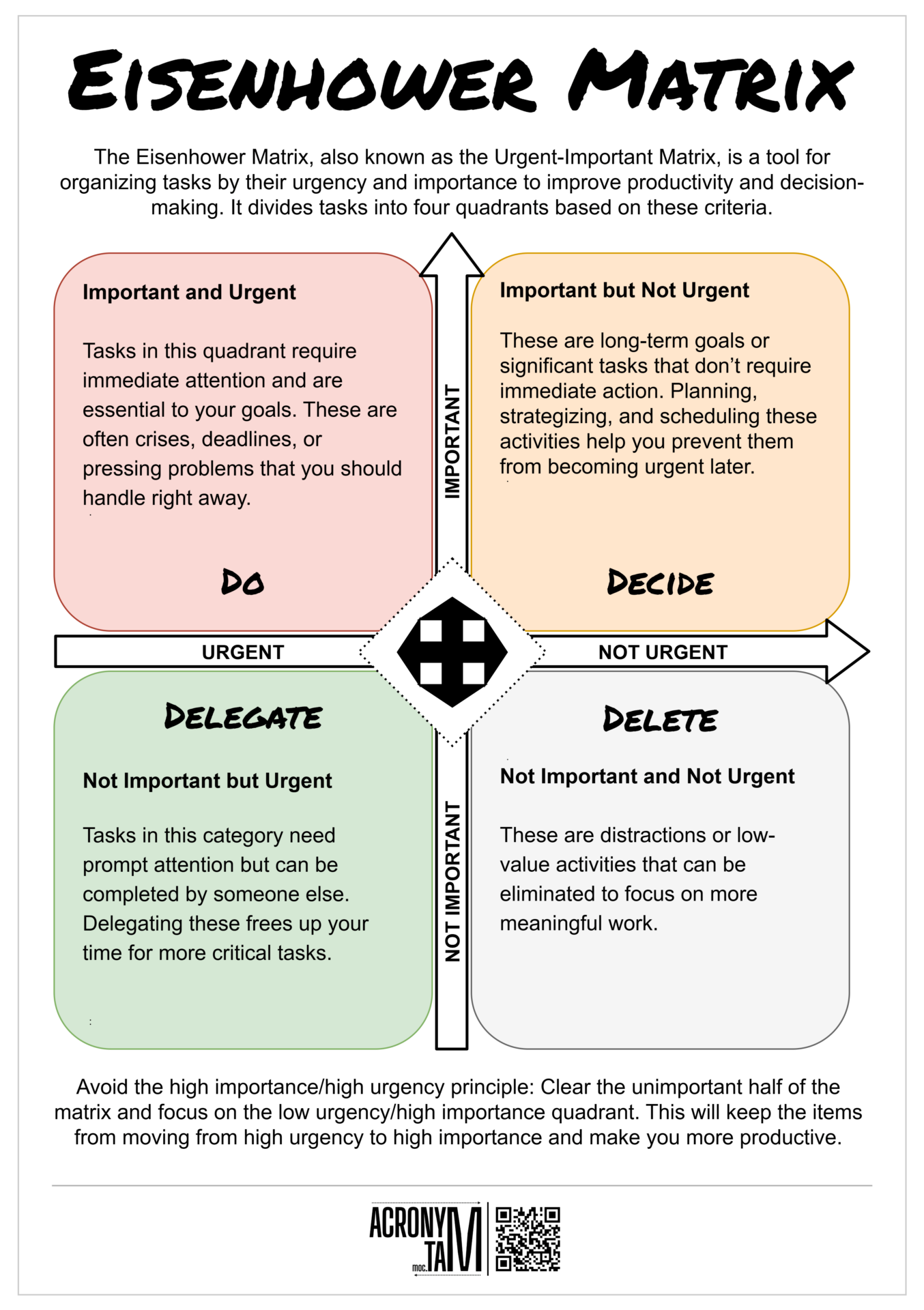
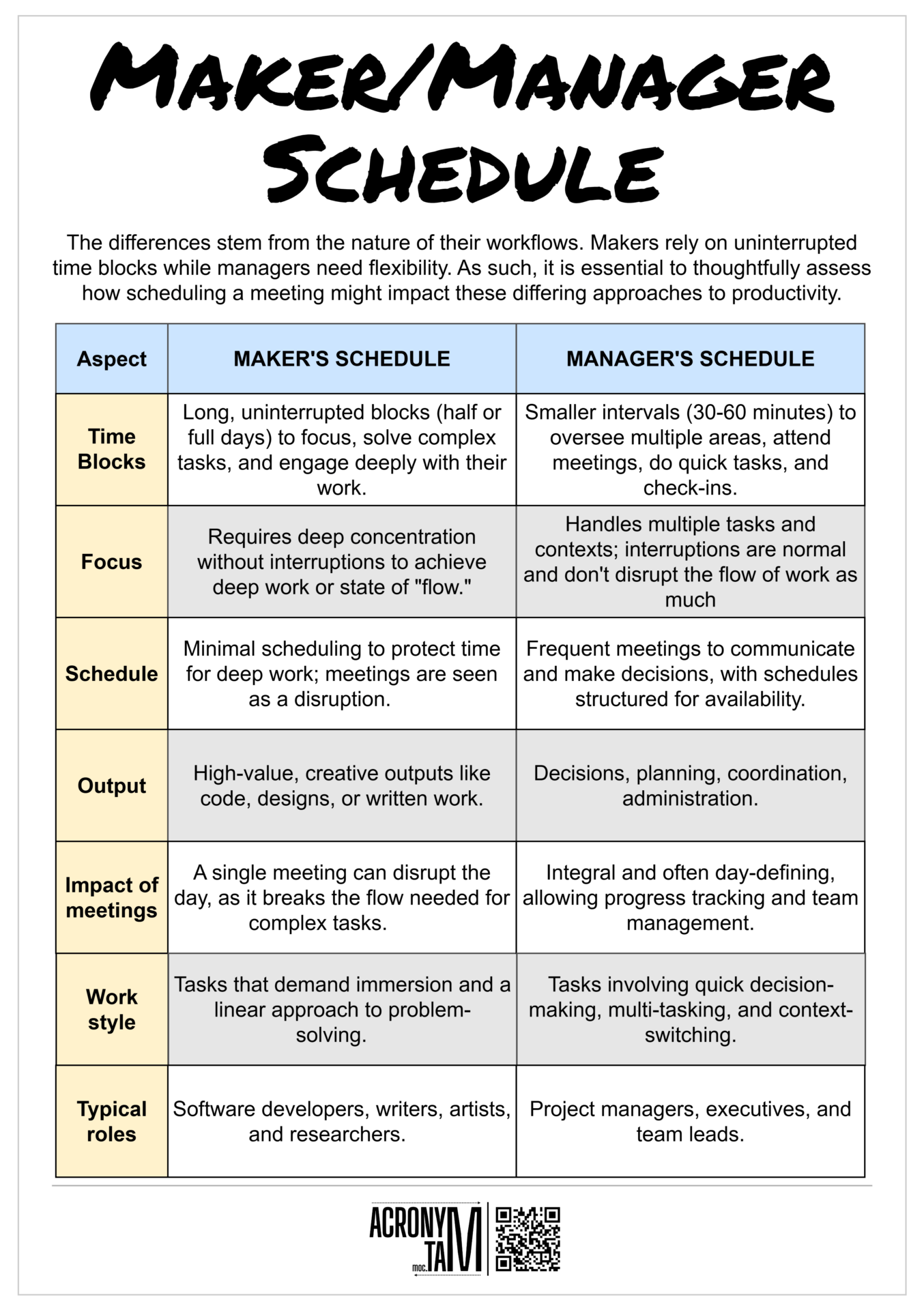
Article
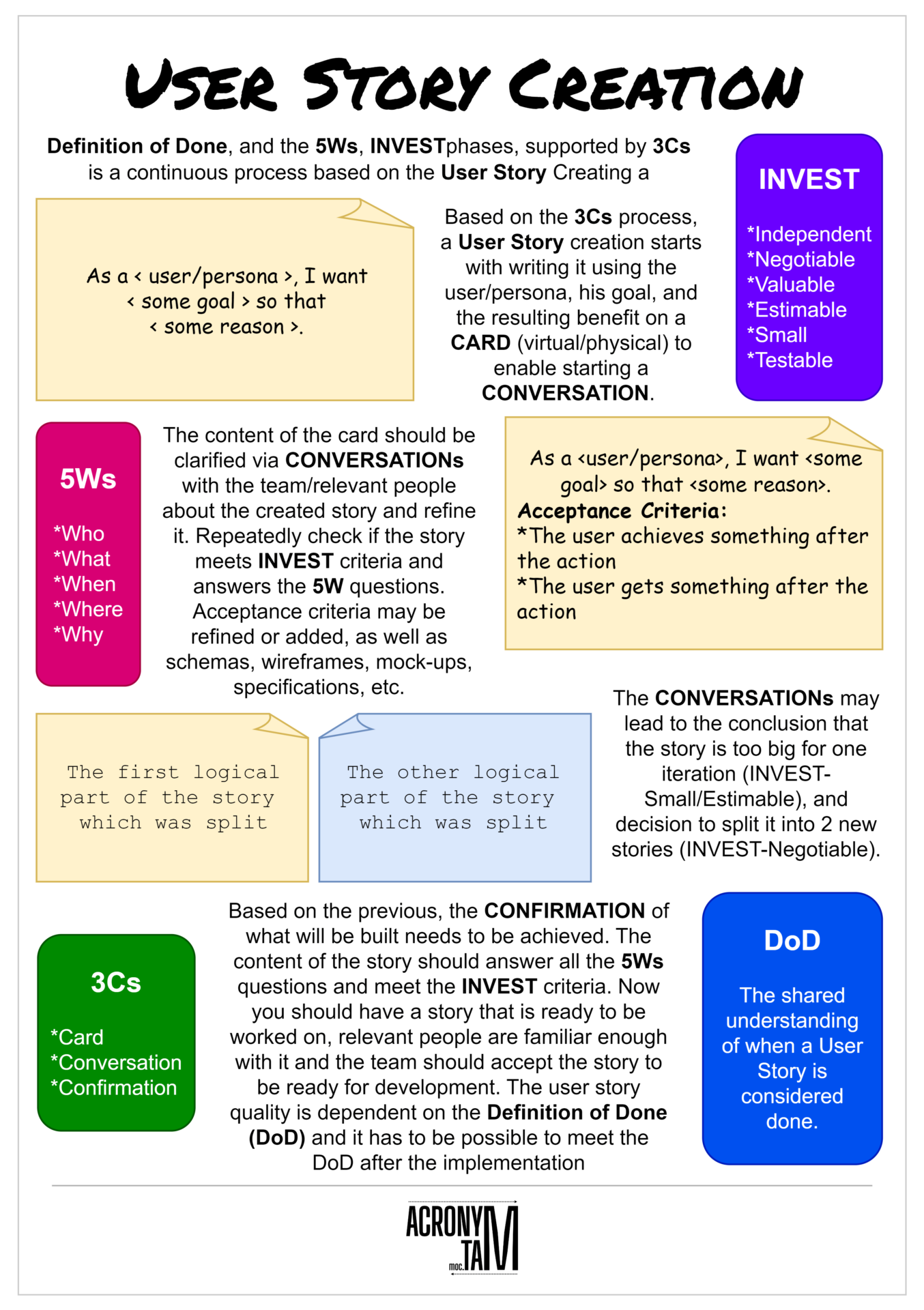
User Story Creation is a continuous process based on the 3Cs phases, supported by INVEST, 5Ws, and the Definition of Done.
Based on the 3Cs process, a User Story creation starts with writing it using the user/persona, his goal, and the resulting benefit on a CARD (virtual/physical) to enable starting a CONVERSATION.

The content of the card should be clarified via CONVERSATIONs with the team/relevant people about the created story and refine it. Repeatedly check if the story meets INVEST criteria and answers the 5W questions. Acceptance criteria may be refined or added, as well as schemas, wireframes, mock-ups, specifications, etc.

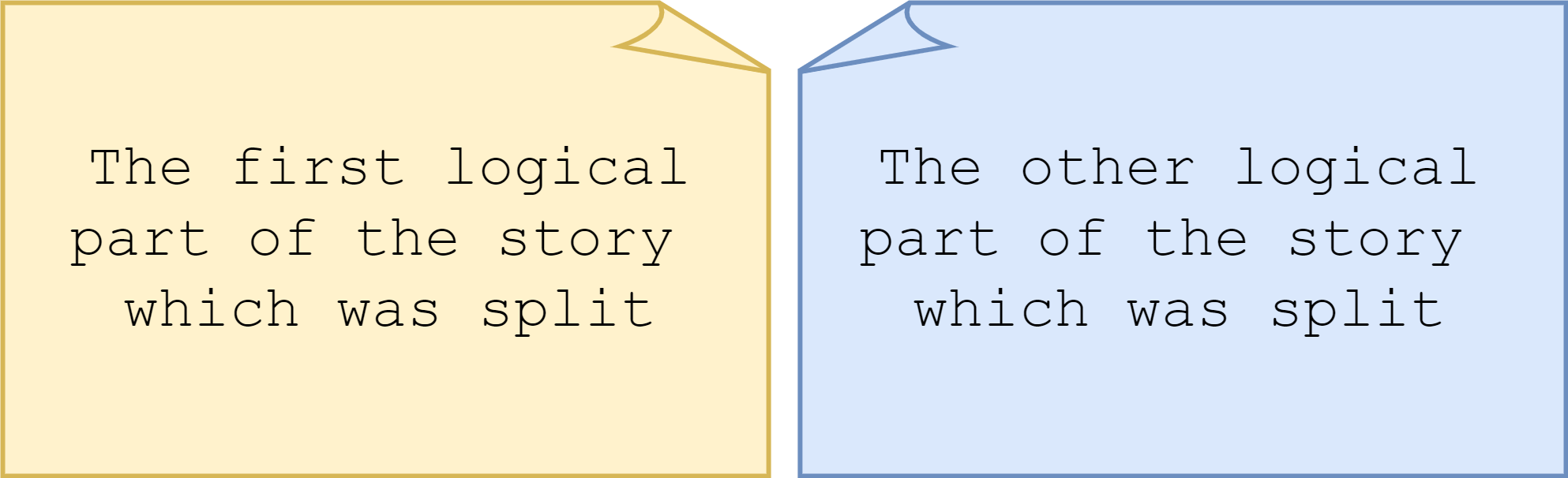
The CONVERSATIONs may lead to the conclusion that the story is too big for one iteration (INVEST-Small/Estimable), and decision to split it into 2 new stories (INVEST-Negotiable).
Based on the previous, the CONFIRMATION of what will be built needs to be achieved. The content of the story should answer all the 5Ws questions and meet the INVEST criteria. Now you should have a story that is ready to be worked on, relevant people are familiar enough with it and the team should accept the story to be ready for development. The user story quality is dependent on the Definition of Done (DoD) and it has to be possible to meet the DoD after the implementation.
Used concepts
INVEST
- Independent
- Negotiable
- Valuable
- Estimable
- Small
- Testable
5Ws
- Who
- What
- When
- Where
- Why
3Cs
- Card
- Conversation
- Confirmation
Definition of Done
The shared understanding of when a User Story is considered done.