Article
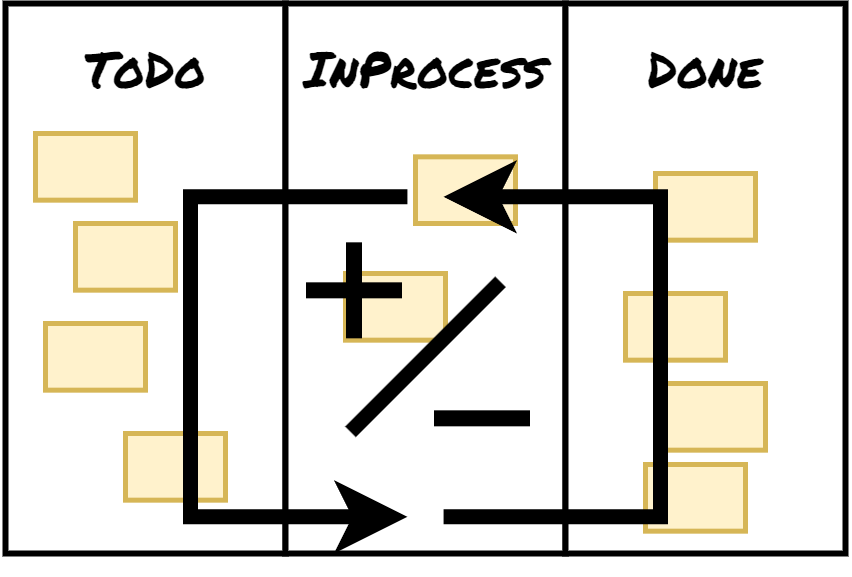
Core Kanban practices:One of the few rules or practices which are the foundation of Kanban are its 3 core practices: Visualize, Limit WIP, and Manage flow. They guide us in Kanban’s way of improvement. Even though there can be more, these are the most important and Ideal to start with.
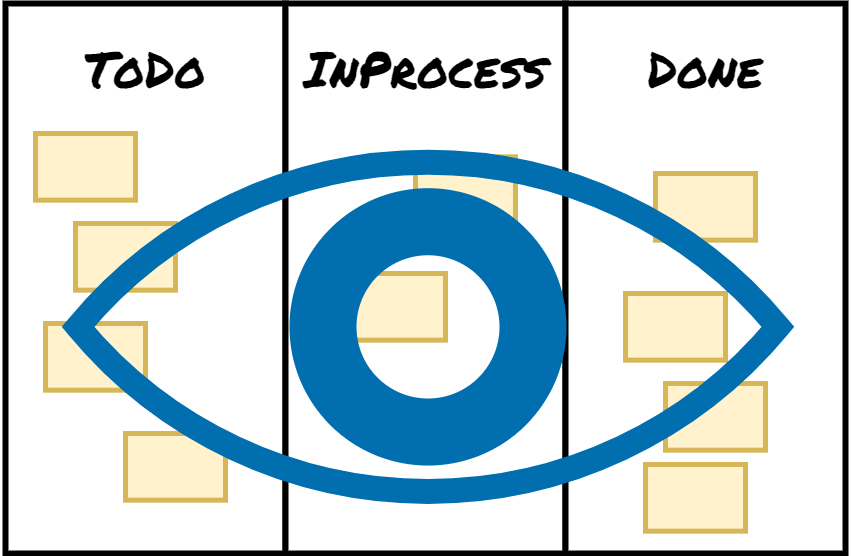
Visualize
Visualizing your work provides transparency, identifying the bottlenecks. Create cards for the items you work on. Think of the workflow – statuses that work items go through to make implicit policies explicit, which enable learning how the work works.
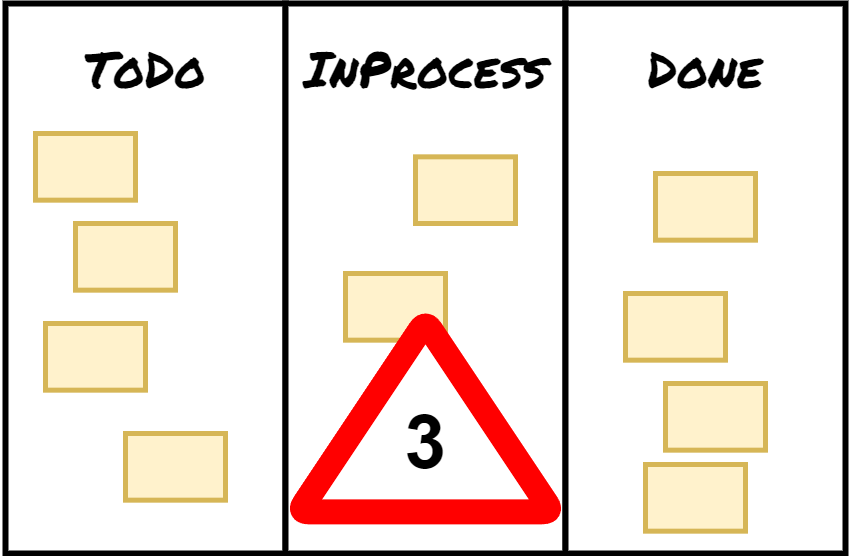
Limit Work In Process
Stop starting, start finishing. Limit the number of items being worked on simultaneously to prevent multitasking and improve efficiency. The smaller number of items will be done faster. Creating tension in the workflow helps to identify issues – improvement opportunities.
Manage flow
The work needs to be managed to solve arising issues in your workflow providing opportunities for improvements. Solving issues based on metrics and bottlenecks in the flow of work enables continuous improvement with the aim to reach an ideal continuous flow.