Article
Situational Leadership Styles
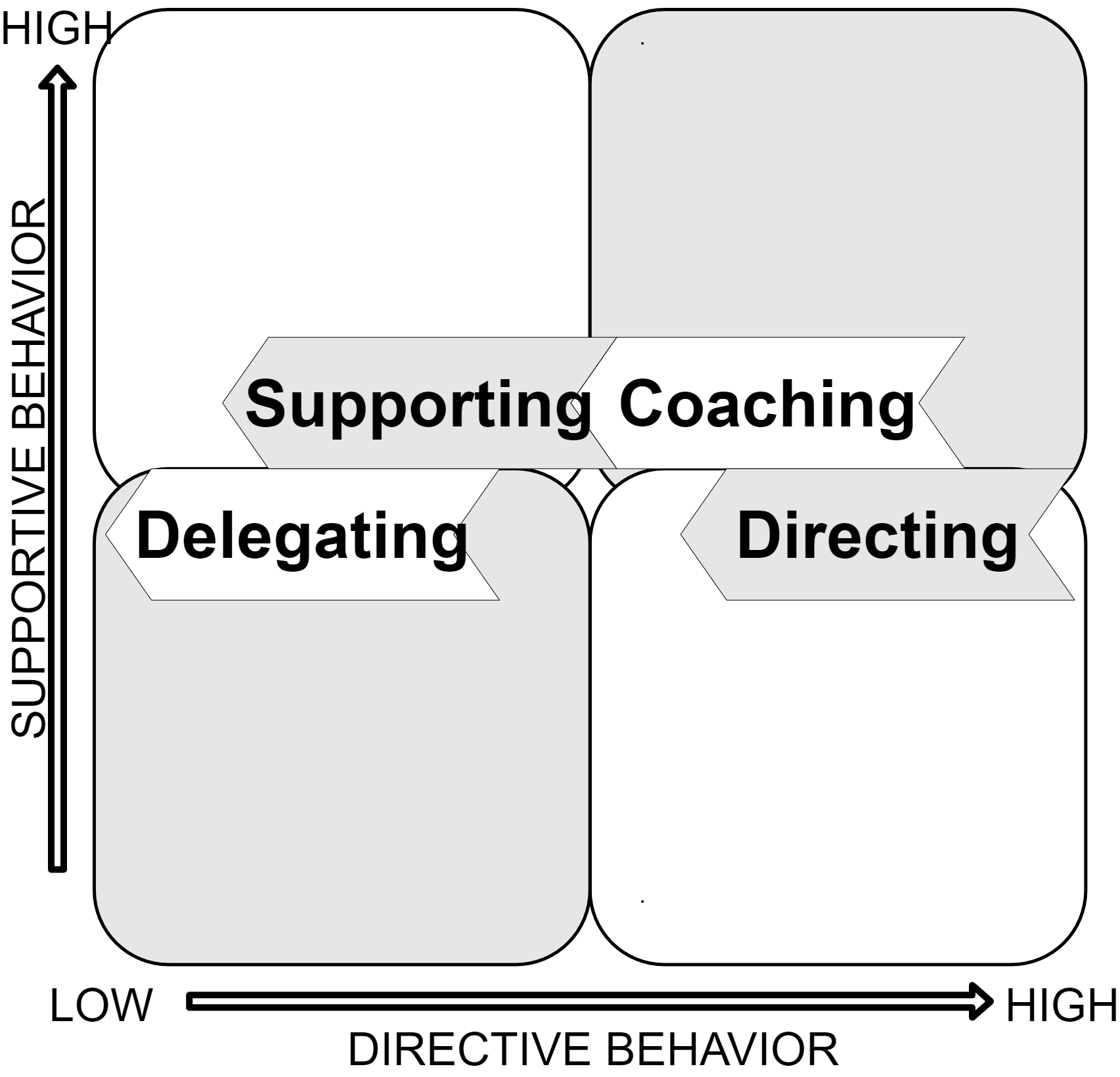
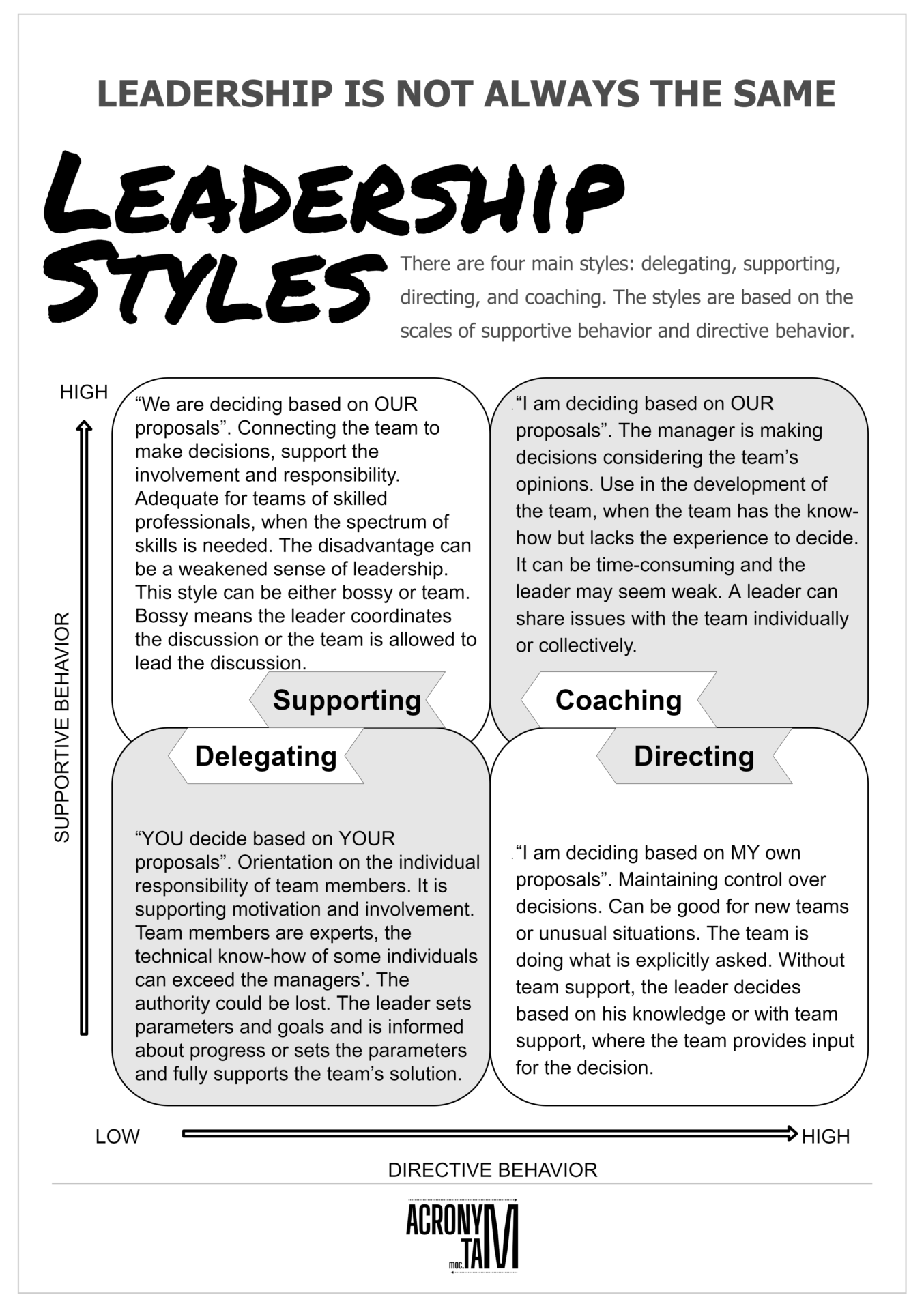
There are four main leadership styles: delegating, supporting, directing, and coaching. The styles are based on the scales of supportive behavior and directive behavior.
Directing style
“I am deciding based on MY own proposals”. Maintaining control over decisions. Can be good for new teams or unusual situations. The team is doing what is explicitly asked. Without team support, the leader decides based on his knowledge or with team support, where the team provides input for the decision.
Coaching style
“I am deciding based on OUR proposals”. The manager is making decisions considering the team’s opinions. Use in the development of the team, when the team has the know-how but lacks the experience to decide. It can be time-consuming and the leader may seem weak. A leader can share issues with the team individually or collectively.
Supporting style
“We are deciding based on OUR proposals”. Connecting the team to make decisions, support the involvement and responsibility. Adequate for teams of skilled professionals, when the spectrum of skills is needed. The disadvantage can be a weakened sense of leadership. This style can be either bossy or team. Bossy means the leader coordinates the discussion or the team is allowed to lead the discussion.
Delegating style
“YOU decide based on YOUR proposals”. Orientation on the individual responsibility of team members. It is supporting motivation and involvement. Team members are experts, the technical know-how of some individuals can exceed the managers’. The authority could be lost. The leader sets parameters and goals and is informed about progress or sets the parameters and fully supports the team’s solution.