Article
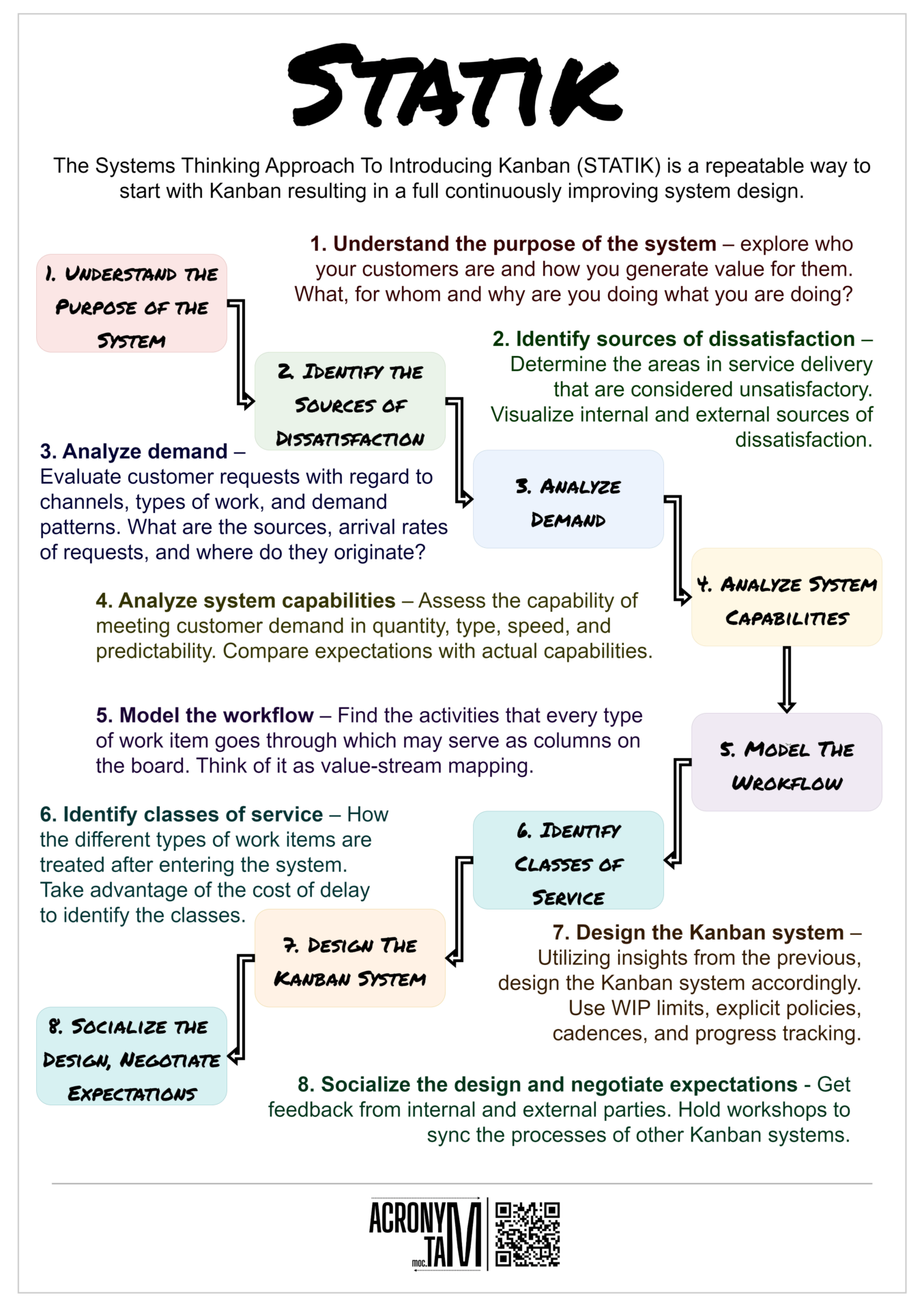
The Systems Thinking Approach To Introducing Kanban (STATIK) is a repeatable way to start with Kanban resulting in a full continuously improving system design.
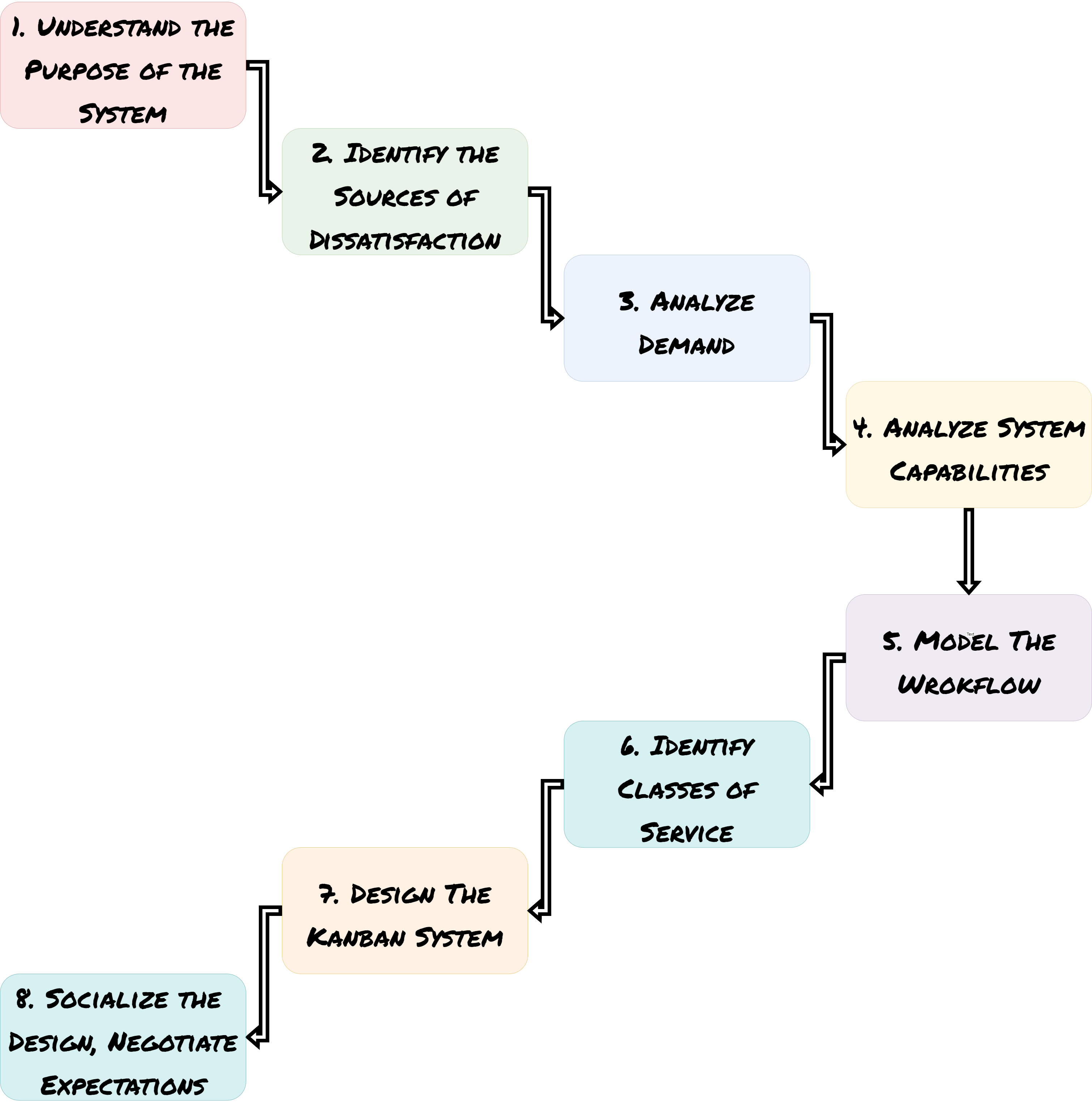
1. Understand the purpose of the system
Explore who your customers are and how you generate value for them. What, for whom and why are you doing what you are doing?
2. Identify sources of dissatisfaction
Determine the areas in service delivery that are considered unsatisfactory. Visualize internal and external sources of dissatisfaction.
3. Analyze demand
Evaluate customer requests with regard to channels, types of work, and demand patterns. What are the sources, arrival rates of requests, and where do they originate?
4. Analyze system capabilities
Assess the capability of meeting customer demand in quantity, type, speed, and predictability. Compare expectations with actual capabilities.
5. Model the workflow
Find the activities that every type of work item goes through which may serve as columns on the board. Think of it as value-stream mapping.
6. Identify classes of service
How the different types of work items are treated after entering the system. Take advantage of the cost of delay to identify the classes.
7. Design the Kanban system
Utilizing insights from the previous, design the Kanban system accordingly. Use WIP limits, explicit policies, cadences, and progress tracking.
8. Socialize the design and negotiate expectations
Get feedback from internal and external parties. Hold workshops to sync the processes of other Kanban systems.
Kanban STATIK Diagram